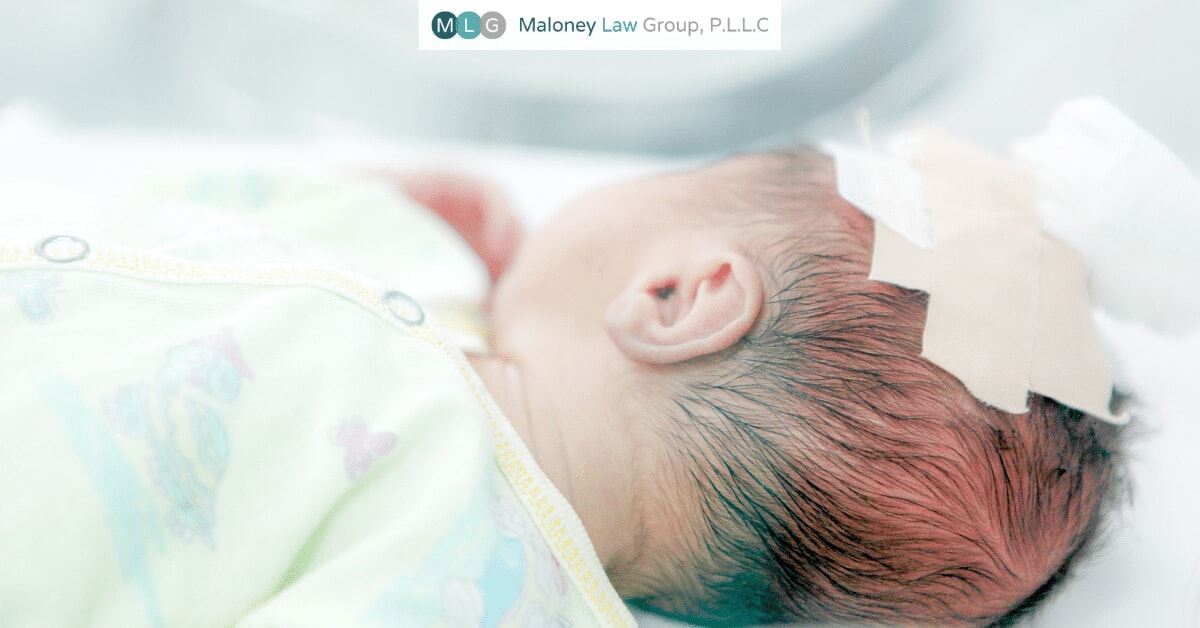
Although there are numerous different causes of infant brain damage, a leading cause of infant brain damage during the labor and delivery process is lack of oxygen to the brain.
During labor, an electronical fetal monitor is typically used to monitor contractions and fetal heart rate. The monitors must be closely watched because fetal heart rate reflects how well a baby is tolerating labor. Decelerations in fetal heart rate indicate that the baby is potentially in distress, and is a sign that a baby is not getting enough oxygen. Both hypoxia (reduced oxygen) and anoxia (no oxygen) may cause a slowing of a baby’s heart rate. When a baby’s brain goes too long without oxygen, brain cells become injured which starts a cycle of injury which can can result in permanent brain damage.
It is essential that doctors and nurses promptly respond to signs of fetal distress during labor and delivery. A failure to do so may result in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) and associated conditions such as cerebral palsy (CP), developmental delays and learning disabilities. Sadly, many times this conditions are caused my preventable medical malpractice.
Uterine hyperstimulation and umbilical cord compression are two complications which cause oxygen deprivation to a baby’s brain during labor and delivery.
Uterine Hyperstimulation
The drug Pitocin is frequently administered to induce labor and increase contractions. Uterine hyperstimulation is a complication of Pitocin usage which can cause oxygen deprivation to a baby’s brain.
The term “Uterine hyperstimulation” refers to contractions which are overly frequent (tachysystole) or abnormally long (hypertonus). During a contraction, blood flow to and from the placenta slows or stops. Between contractions, blood flow then resumes. Without sufficient time between contractions, the placenta does not have time to rest and the baby’s supply of oxygen will diminish, leading to fetal oxygen deprivation.
A serious complication which can result from uterine hyperstimulation is uterine rupture, which can have devastating consequences for both a mother and baby. A uterine rupture is when a mother’s uterus tears. It can cause the placenta to become detached from the uterus, leading to maternal bleeding and oxygen deprivation to the baby. The baby can slip out of the uterus and begin moving toward the abdomen causing suffocation.
When a mother is administered Pitocin, it is essential that doctors and nurses carefully watch electronic fetal monitoring for signs of uterine hyperstimulation and fetal distress. If a mother shows signs of uterine hyperstimulation, Pitocin should be discontinued. In some case, an emergency C-section is required. The failure to respond to hyperstimulation can lead to oxygen deprivation and brain damage.
Umbilical Cord Compression
If the umbilical cord becomes compressed during labor and delivery, it can result in a decrease in blood flow and oxygen to a baby’s brain. While many babies experience mild and temporary umbilical cord compression which is often harmless, there are situation where the compression is more severe and lasts for a prolonged period of time. In these cases, umbilical cord compression can cut off oxygen to the baby.
Lack of oxygen caused by umbilical cord compression can cause signs of fetal distress, including sudden drops in fetal heart rate. Umbilical cord compression requires immediate attention. If it goes unnoticed or is not timely addressed, brain damage can result.
At Maloney Law Group, P.L.L.C., we focus on helping you through the complex aftermath of a birth injury. Our San Antonio birth injury attorneys will be there to give you a voice and fight on your behalf. Let our attorneys be your voice against negligence and pursue the compensation and justice you deserve.
Contact our firm today at (210) 361-2997 to discuss your potential case.



.jpg)
